Aristides Sousa Mendes | 1885 - 1954
Cabanas de Viriato, Portugal
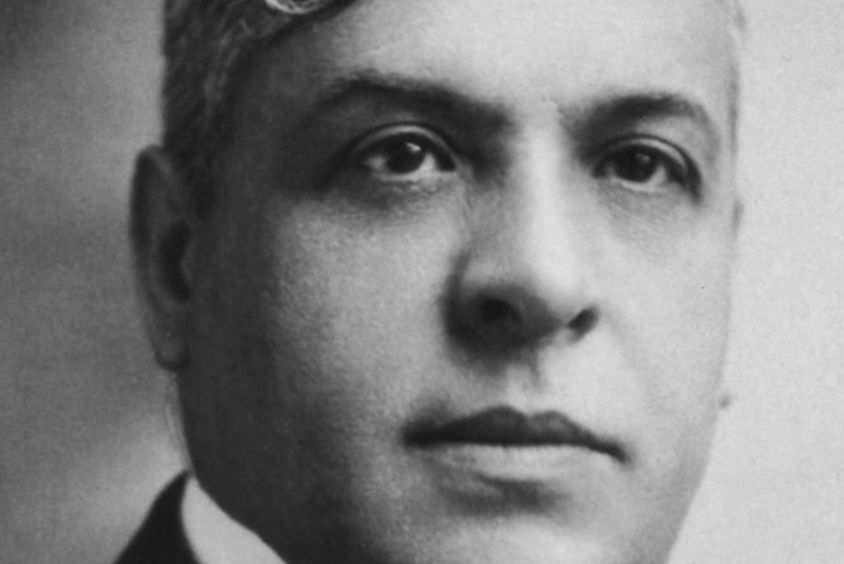
Aristides de Sousa Mendes was a Portuguese diplomat who became known for his courage and humanity during the Second World War. Serving as Portugal's consul in Bordeaux, France, Sousa Mendes risked his career and his own safety by defying the orders of the Portuguese government and issuing thousands of visas to Jews and other refugees fleeing Nazism.
Despite express orders from the Salazar regime to deny visas to refugees, Sousa Mendes followed his conscience and decided to help those facing persecution and death in Nazi-occupied Europe, providing an escape route for thousands of people in danger.
However, his decision to defy the orders of the Portuguese government resulted in his own personal and professional ruin. He was dismissed from the diplomatic service and fell into disgrace, facing financial difficulties for the rest of his life.
Sousa Mendes is remembered as a humanitarian hero who risked everything, saving around 30,000 lives, including entire families.